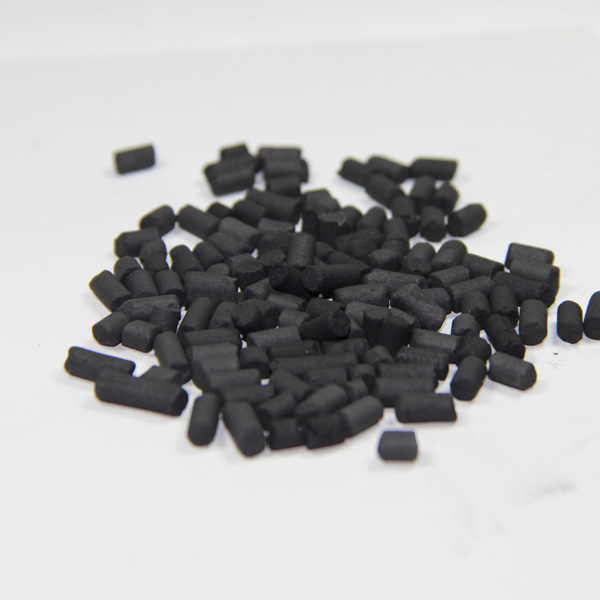
Coal Activated Carbon for Water and Air Purification
What Makes Coal Activated Carbon a Game-Changer in Modern Industries?
Have you ever wondered how industries tackle complex purification challenges while maintaining cost-efficiency and environmental compliance? The answer lies in a versatile material: coal activated carbon. This engineered adsorbent has become indispensable across sectors due to its unmatched capacity to remove contaminants, optimize processes, and support sustainable practices. But what exactly gives it these extraordinary properties, and where is it most effectively deployed?
The Science Behind Coal Activated Carbon
activated carbon">Coal activated carbon is produced through a controlled thermal activation process. High-quality coal undergoes carbonization at temperatures exceeding 600°C in oxygen-deficient environments, followed by steam or chemical activation to create a porous microstructure. This results in a surface area ranging from 500 to 1,500 m²/g – equivalent to covering a football field in a single gram of material.
Three structural features define its efficacy:
Macropores (>50 nm): Act as transport channels for contaminant molecules
Mesopores (2–50 nm): Facilitate molecule distribution
Micropores (<2 nm):Provide primary adsorption sites
This hierarchical pore system enables simultaneous removal of diverse pollutants, from volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to heavy metals.
Key Advantages Over Alternative Adsorbents
While activated carbons derived from coconut shells or wood have specific niches, coal-based variants dominate large-scale applications. Consider these comparative metrics:
| Property | Coal-Based | Coconut-Based | Wood-Based |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Area (m²/g) | 800–1,200 | 900–1,100 | 600–800 |
| Hardness (%) | 90–95 | 70–80 | 50–60 |
| Regeneration Cycles | 5–7 | 3–5 | 2–3 |
| Cost per Ton | $$ | $$$ | $ |
The superior mechanical strength and reactivation potential of coal activated carbon make it ideal for pressurized systems and repetitive use scenarios.
Critical Applications Transforming Industries
Water Treatment: Municipal plants employ coal activated carbon in granular (GAC) or powdered (PAC) forms to address multiple challenges:
Removal of 99.7% of pesticides in drinking water
Reduction of trihalomethanes (THMs) by 80–90%
Extraction of heavy metals like lead and mercury to sub-ppb levels
Air Purification: In industrial gas streams, specialized coal activated carbon products demonstrate:
95% capture efficiency for sulfur compounds
85–92% retention of nitrogen oxides
Complete elimination of hydrogen sulfide odors
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: The material’s ultra-pure grades meet stringent pharmacopeia standards for:

Decolorization of antibiotic solutions
Removal of endotoxins in intravenous drugs
Purification of organic synthesis intermediates
Optimizing Performance Parameters
Selecting the appropriate coal activated carbon requires understanding four critical specifications:
Iodine Number (mg/g): Measures microporosity (800–1,200 optimal for liquid-phase applications)
Molasses Number: Indicates meso/macropore content (200–300 preferred for large molecule adsorption)
Particle Size Distribution: Ranges from 0.15 mm (fine powders) to 3 mm (granules)
Ash Content: Typically 4–10%, with acid-washed grades below 2% for sensitive processes
Future Innovations and Sustainability
Emerging technologies are enhancing coal activated carbon’s capabilities:
Magnetic modification for easy recovery from wastewater
Surface functionalization with amine groups for targeted CO₂ capture
Nanostructured composites achieving 3x higher VOC adsorption
Advanced regeneration methods now recover 95% of adsorption capacity through:
Microwave-assisted thermal reactivation
Supercritical CO₂ cleaning techniques
Catalytic oxidation of adsorbed contaminants
Addressing Common Implementation Challenges
While coal activated carbon offers numerous benefits, users frequently ask:
Q: How long does the material remain effective in continuous operations?
A: Service life ranges from 6 months in aggressive chemical environments to 5+ years in atmospheric filtration, depending on contaminant load and reactivation frequency.
Q: Can it handle emerging contaminants like PFAS?
A> Modified coal activated carbons demonstrate 90–95% removal efficiency for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) at optimized pH conditions.
Q: What safety protocols are essential during handling?
A> Key measures include:
NIOSH-approved respirators for fine particles
Explosion-proof equipment in confined spaces
Humidity-controlled storage below 40% RH
From environmental remediation to precision manufacturing, coal activated carbon continues to evolve as a cornerstone material in industrial purification. Its unique combination of structural integrity, adsorption versatility, and economic viability ensures lasting relevance in an increasingly sustainability-driven market.
- 08-12
What is activated carbon made
Activated carbon is divided into coal and wood activated car...
- 03-18
Where to Buy Bulk Activated Ca
What Is the Secret Behind Large-Scale Pollution Control and ...
- 03-31
Best Activated Carbon Media fo
What Makes Activated Carbon Media the Ultimate Solution for ...
- 10-07
Overcharge performance of acti
Overcharge performance of activated carbon in lithium ion el...